Industries such as energy, oil & gas, mining, manufacturing, and engineering often involve potentially hazardous operations and environments, making it essential to implement effective risk assessment training programs.
This comprehensive guide explores the importance of risk assessment training
for workers in these industries and provides insights into key components and best practices.
We will also introduce you to FAT FINGER, a no-code application builder to help you improve safety management, protect your workers and safeguard your company’s bottom-line.
Why Invest in Risk Assessment Training in Your Company
A comprehensive risk assessment training is an investment in the well-being of both workers and the bottom line.
Ultimately, your company will benefit in the following ways:
Ensuring Worker Safety
The primary objective of risk assessment training is to enhance worker safety. Workers must know the risks associated with their tasks, equipment, and work environments to minimize accidents and injuries.
Compliance With Safety Regulations
High-risk industries are subject to stringent safety regulations and standards. Adequate risk assessment training ensures that workers know and can adhere to these requirements.
Operational Efficiency
Proper risk assessment can identify potential hazards and inefficiencies in work processes.
This information can lead to improved operating procedures, reducing downtime and costs.
Risk Mitigation
Identifying and assessing risks allows organizations to develop strategies for mitigating them. This proactive approach can prevent accidents and protect both workers and the environment.

You may already have a training plan to improve worker safety, increase operational efficiency, mitigate risks, and comply with regulations such as Osha Standards for training requirements.
However, ensuring adherence to such a plan can be tricky without a digital platform to ensure company-wide compliance.
You can digitize training with FAT FINGER, making all the components of risk assessment training discussed in the next section below trackable and available to your frontline teams in minutes.
The data collected through FAT FINGER will help you identify training gaps and take proactive measures to plug them.
5 Key Areas of Risk Assessment Training

Having understood the importance of risk assessment training in your company, let us now explore what risk assessment training entails.
Identifying Hazards
Workers should be trained to recognize and understand the hazards in their work environments. This includes physical hazards (e.g., machinery), chemical hazards (e.g., exposure to toxic substances), biological hazards (e.g., pathogens), and ergonomic hazards (e.g., repetitive motions).
Risk Assessment Methods
Training should cover various risk assessment methodologies, such as the Hierarchy of Controls, Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP), Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA), and Job Safety Analysis (JSA). Workers should learn how to assess risks systematically and prioritize them.
Safety Equipment
Workers should be educated on using personal protective equipment (PPE) and other safety gear properly. This includes understanding when and how to use helmets, gloves, respirators, and safety harnesses.
Emergency Response
High-risk industries require workers to be prepared for emergencies. Training should encompass procedures for responding to fires, chemical spills, accidents, and other critical situations.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is vital in high-risk environments. Workers should learn how to report hazards, incidents, and near-misses promptly. They should also be trained in effective teamwork and collaboration, which is crucial in emergencies.
Communication is also an important aspect of some jobs. For instance, as stated below in Osha training standards, workers in rigging operations should know how to communicate with signal codes.
1915.116 Use of gear (Subpart G-pg 122)
(l) An individual who is familiar with the signal code in use shall be assigned to act as a signalman when the hoist operator cannot see the load being handled. Communications shall be made by means of clear and distinct visual or auditory signals except that verbal signals shall not be permitted.
But how can you guarantee that everyone involved in rigging operations is conversant with each safety signal?
By building a safety checklist in FAT FINGER’s drag-and-drop interface.
You can add all necessary signals in your workflow and have workers tick off every time they use one. If you’re conducting live training sessions, you could capture photos of workers demonstrating their knowledge of signals. Not only is such data relevant for identifying additional training needs, but it’s also handy during audit procedures or if you need to table it to top management during status meetings or to build a business case for additional training budgets.
Best Practices for Risk Assessment Training
Now that you better understand what risk assessment training entails and how it will help your business, let us look at some best practices for risk training.
Digitize
First and foremost, you must do away with manual processes. Customers who have used FAT FINGER report improvements such as improved incident reporting, more control in operations, time savings in procedures, and access to actionable insights.
Tailored Training Programs
Training should be customized to address the specific risks and challenges of each industry and workplace. Generic training may not adequately prepare workers for industry-specific hazards.
Regular Updates
High-risk industries evolve over time, and new risks may emerge. Training programs should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology, regulations, and best practices.
Realistic Simulations
Hands-on training and realistic simulations can enhance the effectiveness of risk assessment training. Workers should have the opportunity to practice risk assessment and emergency response procedures in controlled environments.

Qualified Instructors
Instructors should be experienced and knowledgeable in the industry’s safety protocols and risk assessment methods. They should be able to convey complex information in a clear and understandable manner.
Continuous Learning Culture
Organizations should foster a culture of continuous learning and safety consciousness. Workers should be encouraged to seek ongoing training and to share their knowledge and experiences with colleagues.
Build Risk Assessment Training Workflows with FAT FINGER
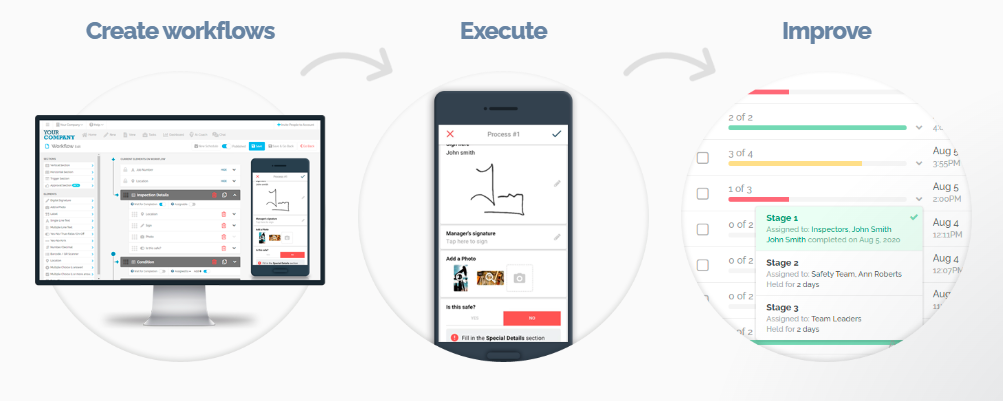
Risk assessment training for workers is not only a legal requirement but also a moral imperative. The safety of workers and the protection of the environment depend on the effectiveness of these programs.
With FAT FINGER, you can effectively identify hazards, assess risks, implement appropriate safety measures and thereby significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
FAT FINGER offers:
Easy-to-use interface: Workers can promptly and accurately document testing through an easy-to-use interface even in high-pressure industrial environments, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Data-Driven Insights: The software compiles risk analysis data to generate comprehensive reports and visualizations, empowering organizations to make informed decisions.
Integrated Workflows: FAT FINGER seamlessly integrates incident reporting into existing industrial workflows, ensuring a cohesive approach to safety and operational excellence.
Real-Time Collaboration: FAT FINGER facilitates instant communication between your team, supervisors, and management, expediting response times and fostering collaboration.


