A Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) is an essential component of welding safety as it is concerned with identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks.
This blog explores the hazards common in welding and provide tips for conducting a Job Hazard Analysis.
Understanding Welding Hazards
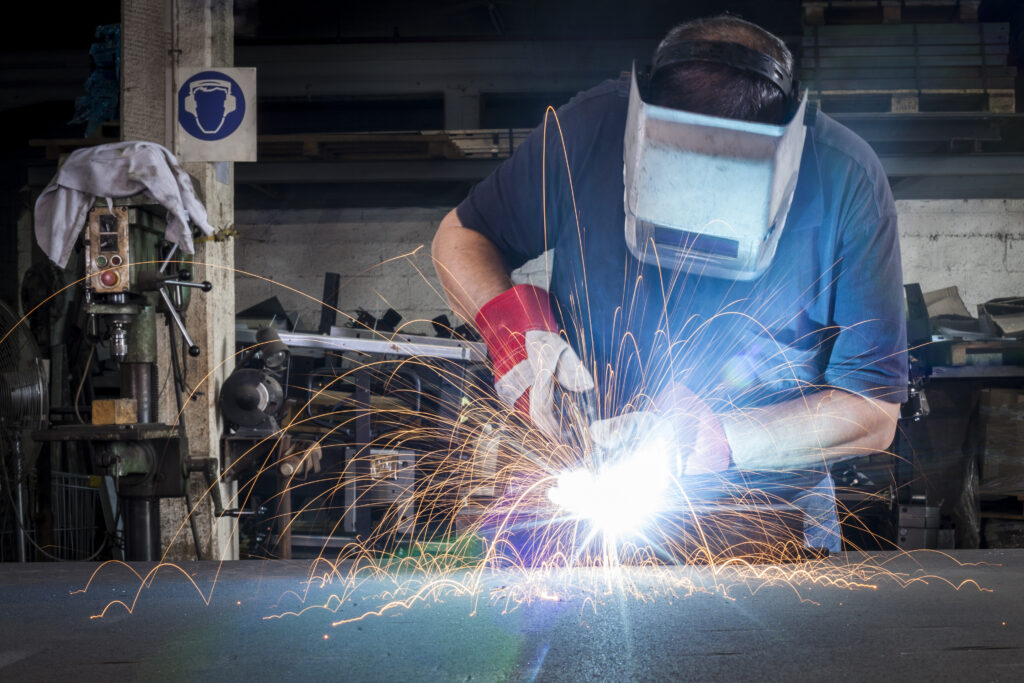

Welding is a crucial industrial process in various sectors, from construction and manufacturing to automotive and aerospace.
While it plays a vital role in creating strong, lasting connections, it also poses significant hazards to the individuals performing the task.
Before we delve into the specifics of Job Hazard Analysis, let’s first understand some common welding hazards:
Electric Shock: Welding involves high-voltage electricity, and improper handling of welding equipment can result in severe electric shocks.
Fire and Explosion: The intense heat generated during welding can ignite flammable materials, causing fires or even explosions.
Exposure to Harmful Fumes and Gases: Welding produces fumes and gases that, if inhaled, can lead to respiratory problems, dizziness, and even long-term health issues.
UV Radiation: The intense light emitted during welding can cause eye damage or “welder’s flash” if proper eye protection isn’t used.
Burns and Injuries: Molten metal, sparks, and hot surfaces can cause burns, eye injuries, and other physical harm to welders.
The Importance of Job Hazard Analysis
Job Hazard Analysis is a structured process aimed at identifying and mitigating these and other risks associated with welding. Here’s why it’s so crucial:
Prevention of Accidents: JHA helps prevent accidents by systematically identifying potential hazards and taking steps to eliminate or control them.
Worker Safety: Ensuring the safety of welders and other personnel should be your top priority. JHA can help you create a safer work environment.
Steps for Conducting a Job Hazard Analysis in Welding

The following are the steps involved in conducting a Job Hazard Analysis for welding:
Step 1 -Identify the Task
Define the specific welding task or job you want to analyze. This could include different types of welding, such as arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, or oxy-acetylene welding.
Step 2 -Break Down the Task
Divide the welding task into its steps. For welding, these steps might include preparing the materials, setting up the welding equipment, performing the welding, and post-weld cleanup.
Step 3 -Identify Hazards
For each step, identify potential hazards. Refer to the list of common welding hazards mentioned earlier to guide you.
Step 4 -Assess Risks
- Evaluate the risks associated with each identified hazard.
- Consider the likelihood of each risk and its severity.
- Assess who might be affected, including the welder and nearby workers.
Step 5: Implement Controls
Develop and implement controls to mitigate or eliminate the identified hazards. Such strategies can include:
- Using personal protective equipment (PPE) like welding helmets, gloves, and safety glasses.
- Ensuring enclosed work areas are properly ventilated
- Properly grounding welding equipment to prevent electrical shocks.
- Installing fire-resistant barriers or shielding materials to prevent fires.
- Establishing safe welding zones with restricted access to unauthorized personnel.
- Providing training and ensuring welders are certified
Use FAT FINGER to Manage Job Hazards
Identifying and mitigating job hazards doesn’t have to be complicated or costly. Not when you have FAT FINGER.
Why use FAT FINGER?
- It’s a no-code drag and drop safety workflow builder
- Anyone in your organization can use it to build workflows
- It’s automated
- Mobile and desktop friendly
- AI coach