As industries continue to evolve, the need for efficient and effective inspection methods becomes increasingly crucial. One such method that has gained significant traction in recent years is thermal imaging. This technology, when combined with the power of digital workflow solutions like FAT FINGER, can revolutionize material inspection processes across various sectors.
What is Thermal Imaging?
Thermal imaging, also known as thermography, is a non-contact technology that allows the visualization of temperature variations. It uses infrared radiation to detect heat patterns, changes, and heat leaks in materials, making it an invaluable tool in material inspection.
Applications of Thermal Imaging in Material Inspection

Thermal imaging has a wide range of applications in material inspection. Here are a few examples:
- Quality Control: Thermal imaging can identify defects in products or structures that may not be visible to the naked eye. This is particularly useful in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and aerospace.
- Predictive Maintenance: By identifying hot spots in machinery, thermal imaging can predict potential failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
- Safety Inspections: Thermal imaging can detect heat leaks or insulation failures in facilities, contributing to a safer working environment.
When integrated with a digital workflow solution like FAT FINGER, thermal imaging can be even more effective. FAT FINGER’s easy-to-use platform allows front-line teams to build checklists and workflows that incorporate thermal imaging data, ensuring work is done correctly every time.
Challenges of Thermal Imaging in Material Inspection
Despite its numerous benefits, thermal imaging is not without its challenges. These include:
- High Initial Costs: Thermal imaging equipment can be expensive, making it a significant investment for many companies.
- Training Requirements: Proper use of thermal imaging technology requires specialized training, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Interpretation of Results: Interpreting thermal images can be complex and requires expertise to ensure accurate results.
However, these challenges can be mitigated with the right tools and strategies. For instance, FAT FINGER’s digital workflow builder can simplify the process of incorporating thermal imaging data into daily operations, reducing the need for extensive training. Furthermore, its AI coaching feature can assist in interpreting results, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Case Study: FAT FINGER and Thermal Imaging
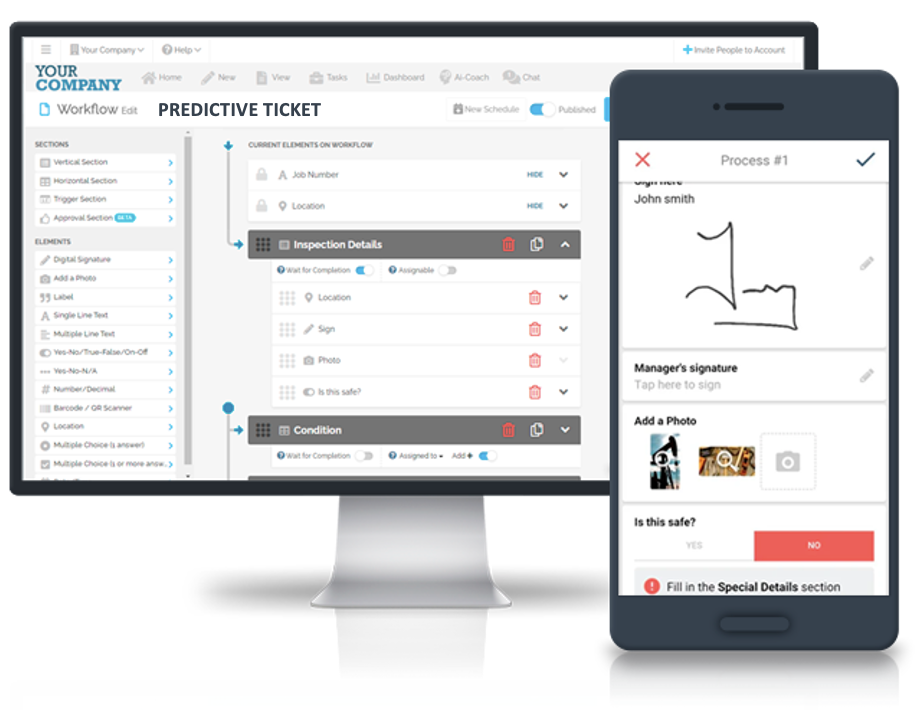
One example of the successful integration of thermal imaging and FAT FINGER’s digital workflow solution is in the field of predictive maintenance. By incorporating thermal imaging data into FAT FINGER’s preventive maintenance inspection workflows, a manufacturing company was able to identify potential equipment failures before they occurred, reducing downtime and saving costs.
Conclusion
Thermal imaging is a powerful tool in material inspection, offering numerous benefits such as improved quality control, predictive maintenance, and enhanced safety. However, to fully leverage this technology, it must be integrated into a robust digital workflow solution like FAT FINGER. Despite the challenges, the potential of thermal imaging in material inspection is vast, and with the right tools and strategies, it can significantly contribute to operational excellence.
Ready to revolutionize your material inspection processes with thermal imaging and FAT FINGER? Sign up today or request a demo to see how FAT FINGER can empower your front-line teams to do their work correctly every time.


