Journey reports and incident reports play a significant role in documentation and reporting across different industries and scenarios. These reports serve unique purposes, capturing diverse aspects of processes, projects, and unexpected events.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the characteristics, content, and applications of journey reports and incident reports. The comparison table at the end of this article summarizes the characteristics and purpose of these two reports.
Journey Reports

A journey report is a comprehensive narrative that unfolds the story of a project or an undertaking from initiation to conclusion.
Unlike incident reports, which are reactive and respond to unexpected events, journey reports are proactive, aiming to provide a holistic view of the entire journey.
The primary purpose of a journey report is to document the progression of a project, offering insights into the challenges faced, milestones achieved, and lessons learned.
The Content of a Journey Report
The content of a journey report is diverse and covers the following aspects of the project:
- A chronological account of events serves as the backbone, allowing stakeholders to trace the evolution of the project over time.
- Key achievements and breakthroughs acknowledge and celebrate success.
- An analysis of challenges and obstacles encountered during the journey provides valuable information for future planning and decision-making.
Structure of a Journey Report:
While the structure of journey reports may vary depending on the nature of the project, they generally include the following key elements:
- An introduction outlining the purpose and scope of the journey report.
- The main body provides a chronological account of events, achievements, challenges, and lessons learned.
- A conclusion summarizes the key takeaways and often includes recommendations for future endeavors.
- Appendices may be added to provide supplementary information, such as detailed data sets or supporting documents.
Incident Reports
In contrast to journey reports, incident reports are reactive. They are designed to capture details about unexpected events, accidents, or issues that disrupt the normal course of operations. Such events may include workplace accidents, equipment malfunctions, security breaches, and other incidents that may jeopardize safety.
The primary purpose of an incident report is to:
- Analyze the incident
- Understand its root causes, and
- Implement corrective actions to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Incident reports play a crucial role in safety management, quality assurance, and overall risk mitigation.
The Content of an Incident Report
The content of an incident report is focused on the specific incident that occurred. It includes essential details such as:
- The date and time of the incident
- The individuals involved
- A description of what happened
- The impact of the incident on operations
- Immediate actions taken to address the situation
Incident reports are not only a record of past events but also serve as a tool for organizational learning and improvement.
Structure of an Incident Report
Similar to journey reports, incident reports follow this structured format:
- An introduction outlining the purpose of the report and providing context for the incident.

- The main body detailing the incident, including the who, what, when, where, and how.
- An analysis of the incident, including root cause identification, is a critical component.
- A conclusion summarizing the findings and providing recommendations for preventive measures.
- Appendices may contain additional supporting documents, such as witness statements or photographs.
Now that we have explored the individual characteristics of journey reports and incident reports let’s delve into a comparative analysis to highlight the distinctions between the two types of documentation.
Below is a side-by-side comparison table highlighting the key differences between journey reports and incident reports:
Comparison Table of Journey Reports vs Incident Reports
| Aspect | Journey Reports | Incident Reports |
| Definition | Comprehensive narrative documenting the entire project or journey. | Focused documentation capturing details of specific incidents. |
| Purpose | Proactively provides a holistic view of the entire journey, focusing on progress, achievements, and challenges. | Reactively captures details about unexpected events, aiming to understand causes and implement corrective actions. |
| Temporal Perspective | Longitudinal, covering the entire duration of the project or journey. | Snapshot, focusing on specific moments in time when incidents occur. |
| Proactivity vs. Reactivity | Proactive, initiated to document planned progress and outcomes. | Reactive, generated in response to unplanned and unforeseen events. |
| Scope of Information | Comprehensive and broad, covering successes, challenges, and lessons learned. | Specific and focused, concentrating on the details of a particular incident. |
| Audience and Stakeholders | Intended for a diverse audience, including project stakeholders, executives, and those interested in the entire journey. | Primarily targeted at safety officers, quality assurance teams, and individuals responsible for risk management. |
| Use in Decision-Making | Informs decision-making for future projects, providing insights and recommendations based on documented experiences. | Drives decisions related to safety protocols, risk management, and preventive measures to avoid similar incidents. |
| Example Use Cases | Business projects, research expeditions, long-term assignments, and development initiatives. | Workplace accidents, equipment malfunctions, security breaches, and unexpected events impacting operations. |
| Structure | Typically includes an introduction, main body (chronological account, achievements, challenges), conclusion, and appendices. | Generally consists of an introduction, main body (incident details, analysis, conclusions), and appendices with supporting documents. |
Final Words: Journey Reports vs Incident Reports; Which Should You Choose?
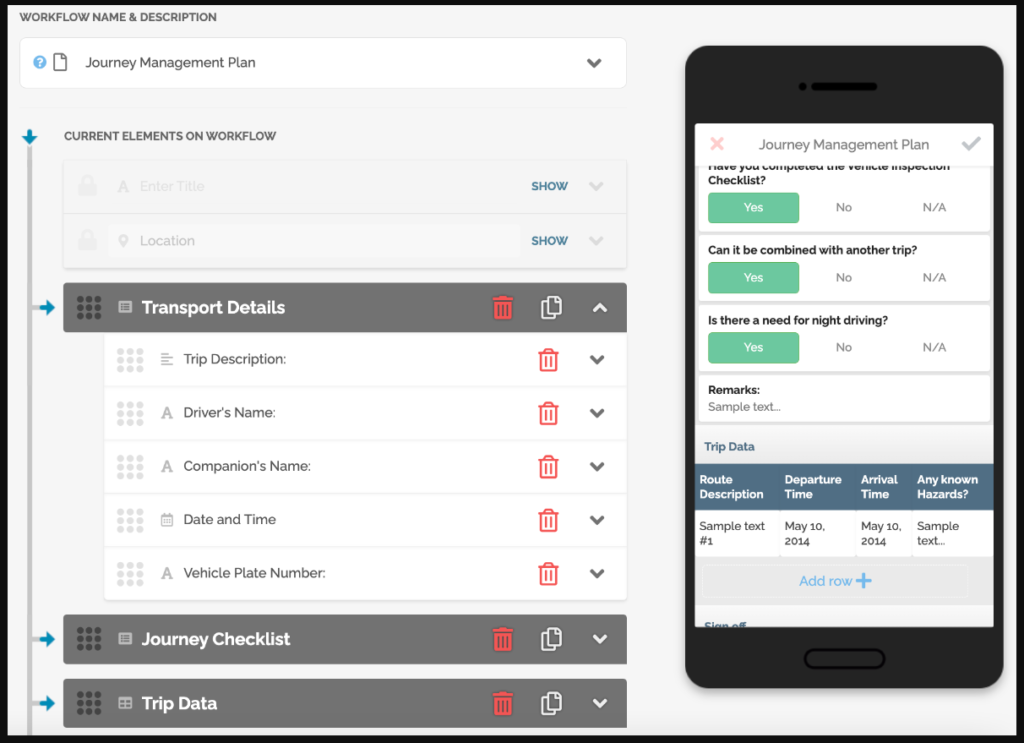
Journey reports and incident reports are indispensable tools in the realm of documentation, each playing a distinct role in capturing the dynamic nature of projects and unexpected events.
- Journey reports provide a panoramic view of the entire journey, celebrating successes and analyzing challenges
- Incident reports focus on the granularity of specific incidents, aiming to enhance safety, quality, and overall operational resilience.
By utilizing both journey reports and incident reports, you can create a robust documentation framework that not only preserves historical records but also facilitates continuous improvement.
Streamline Your Journey Reports and Incident Reports with FAT FINGER
FAT FINGER is a revolutionary platform designed to transform the way you organize and manage journey reports and incident reports. With our intuitive Drag & Drop Workflow Builder, you can effortlessly customize workflows to suit your specific reporting needs. Whether on mobile or desktop, our user-friendly interface ensures seamless navigation, making reporting a breeze.
Features of FAT FINGER:
- Drag & Drop Workflow Builder
- Mobile & Desktop Workflows
- Workflow
- Dashboards
- Integrations
- Augmented Reality
- Connect IoT Devices
- Artificial Intelligence Coaching
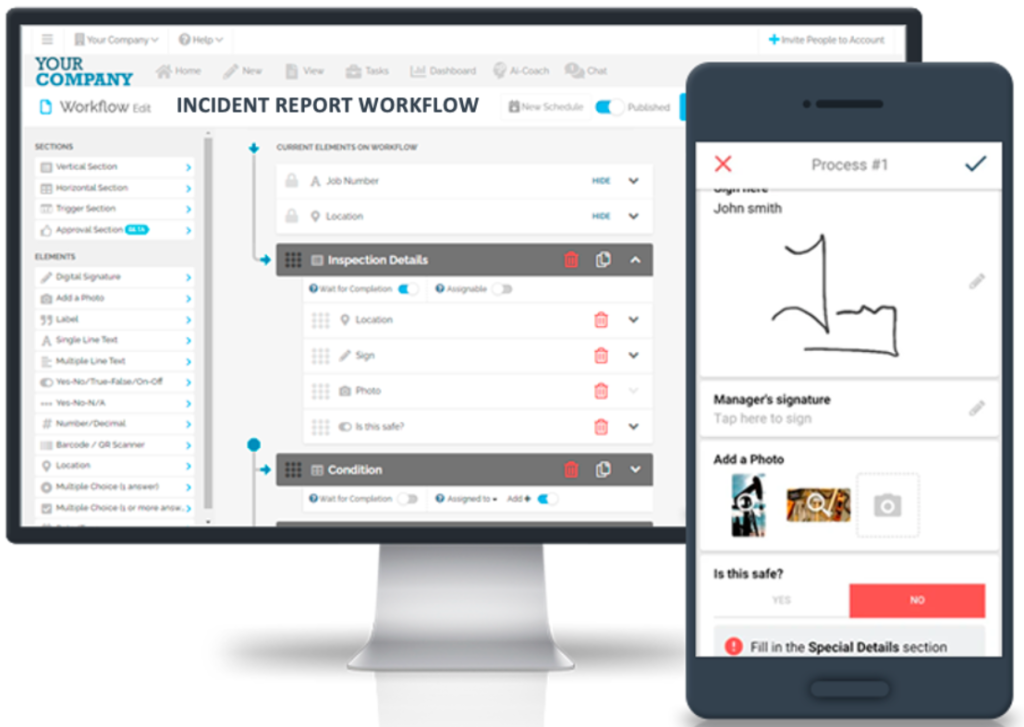
Take the first step towards a more efficient, transparent, and proactive reporting culture. Join FAT FINGER today and elevate your incident reporting to new heights!


