In the world of manufacturing, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) stand as a cornerstone, ensuring that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. It’s a concept that transcends industries, touching everything from pharmaceuticals to food production, and is vital for both safety and compliance.
Understanding GMP is crucial not only for compliance with regulations but also for the success and integrity of a business. As such, this guide aims to delve deep into the nuances of Good Manufacturing Practices, offering insights, practical advice, and a holistic view of its application across various sectors. Whether you’re new to the concept of GMP or looking to refine your practices, this comprehensive exploration will serve as your essential resource.
Why GMP Matters?
- Safety: At its core, GMP ensures the safety of products, reducing the risk of contamination, mix-ups, and errors.
- Compliance: Adhering to GMP guidelines is not optional; it’s a regulatory requirement in many industries, especially in pharmaceuticals and food production.
- Quality: GMP is synonymous with quality, ensuring that products are consistently produced according to the highest standards.
- Consumer Trust: By following GMP, manufacturers can build and maintain consumer trust, a crucial element in today’s competitive market.
Understanding Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are more than just a set of guidelines; they are the heartbeat of a robust, quality-driven manufacturing process. At its core, GMP encompasses a wide array of practices and principles designed to ensure that products are made consistently and controlled to the quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
What Are Good Manufacturing Practices?
GMP represents a comprehensive approach to manufacturing, enabling companies to minimize or eliminate instances of contamination, mix-ups, and errors. This in turn protects the consumer from purchasing a product which is not effective or even dangerous. Implementation of GMP requirements entails quality management, control, and assurance practices, facility and equipment maintenance, raw material verification, and personnel training.

The Goals and Objectives of GMP
The primary aim of GMP is to ensure product quality and safety. This involves a multipronged approach:
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that products are manufactured under conditions and practices required by the GMP guidelines.
- Risk Minimization: Reducing the risks inherent in any pharmaceutical production that cannot be eliminated through testing the final product.
Key Components of GMP
- Quality Management Systems: These systems are the backbone of GMP, ensuring that processes are defined, controlled, and continuously improved.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Accurate and detailed documentation ensures traceability and accountability, making it possible to investigate and rectify any issues that arise.
- Sanitation and Hygiene: A fundamental element of GMP, particularly in food and pharmaceutical manufacturing, to prevent contamination.
- Equipment Verification and Validation: Ensuring that machinery and equipment are up to the task of producing quality products.
- Personnel Qualifications and Training: Skilled, knowledgeable staff are essential for maintaining GMP standards.
The Global Impact of GMP
Good Manufacturing Practices are not confined by borders; their influence spans the globe, impacting international trade, regulatory environments, and consumer confidence.
GMP Regulations Around the World
Different countries have their own regulatory frameworks for GMP, but the core principles remain consistent. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets the standards, while in Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) takes the lead. Other global players include the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), which work towards harmonizing the standards across countries.

The Role of International Organizations in GMP
Organizations like WHO and ICH play a crucial role in establishing international GMP guidelines, facilitating trade and regulatory compliance across borders. Their efforts ensure that no matter where a product is made, if it’s GMP-certified, it adheres to a universally recognized standard of quality.
Implementing GMP in Manufacturing Operations
Adopting Good Manufacturing Practices is a strategic investment in quality and compliance. Here’s how companies can implement GMP in their manufacturing operations:
Steps to Achieve GMP Compliance
- Assessment: Evaluate current practices against GMP standards to identify gaps.
- Planning: Develop a detailed action plan to address deficiencies and enhance compliance.
- Training: Equip staff with the necessary knowledge and skills through comprehensive training programs.
Common Challenges and Solutions in GMP Implementation
- Documentation: Maintaining thorough documentation can be daunting. Implementing a robust document management system can streamline this process.
- Quality Control: Establishing effective quality control measures requires both technology and skilled personnel. Investing in both is key to success.
Best Practices for Maintaining GMP Compliance
- Continuous Training: Ongoing education ensures that staff stay abreast of the latest GMP standards and practices.
- Regular Audits: Frequent audits help identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
Introducing FAT FINGER: Enhancing GMP Compliance
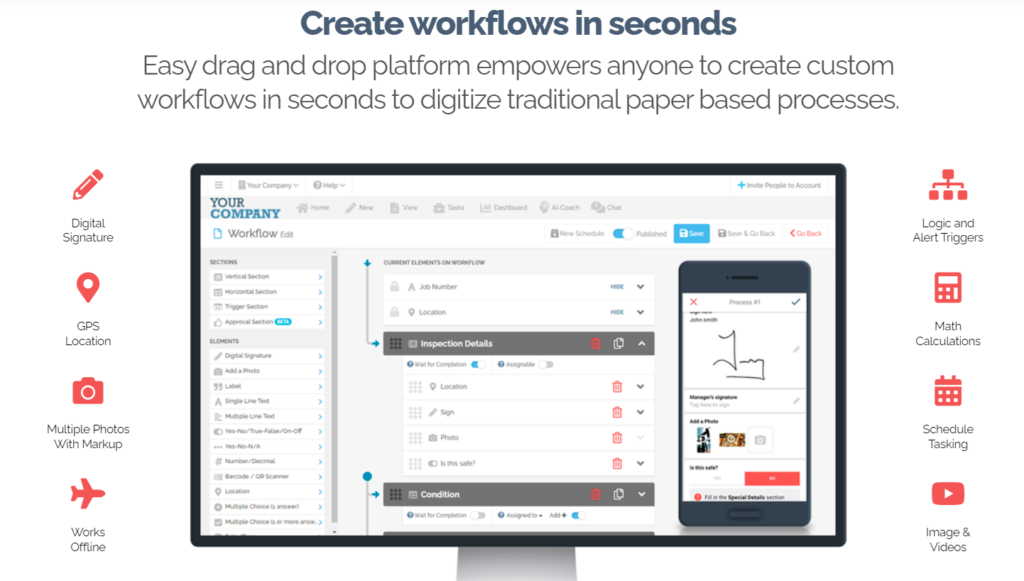
FAT FINGER is an intuitive, user-friendly platform that empowers teams to create, manage, and report on safety and quality procedures effortlessly. It bridges the gap between the stringent requirements of GMP and the dynamic, fast-paced nature of modern manufacturing environments. Here’s how FAT FINGER aligns with the principles of Good Manufacturing Practices:
- Digital Documentation and Record-Keeping: FAT FINGER facilitates easy documentation, allowing for the digital capture and storage of records. This feature is crucial for GMP, where accurate and accessible records are essential for compliance, audits, and traceability.
- Streamlined Quality Control Processes: With FAT FINGER, you can standardize quality control procedures across your operations, ensuring consistency and compliance with GMP standards. The software enables real-time monitoring and reporting, making it easier to identify and address issues promptly.
- Enhanced Training and Communication: FAT FINGER’s collaborative platform enhances communication and training among team members. By providing easy access to GMP guidelines, SOPs, and training materials, the software ensures that all personnel are well-informed and up-to-date with the latest GMP requirements.
- Audit and Inspection Readiness: The software simplifies the preparation for audits and inspections by organizing all necessary documentation and records in an easily accessible format. This readiness can significantly reduce the stress and workload associated with GMP audits, ensuring a smoother, more efficient process.
The Role of FAT FINGER in Supporting GMP
By integrating FAT FINGER into their operations, manufacturers can achieve several key benefits:
- Efficiency: Automate and streamline GMP-related processes, reducing manual effort and the potential for human error.
- Compliance: Maintain up-to-date records and ensure adherence to GMP standards, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
- Quality Assurance: Enhance product quality and safety by implementing consistent, standardized procedures across all stages of manufacturing.
- Operational Visibility: Gain real-time insights into GMP compliance and quality control measures, enabling proactive management and continuous improvement.
In conclusion, FAT FINGER is not just a tool for enhancing safety management; it’s a comprehensive platform that supports the rigorous demands of Good Manufacturing Practices in the manufacturing sector. By leveraging FAT FINGER, companies can ensure that their commitment to quality, safety, and compliance is not only met but exceeded, paving the way for excellence in manufacturing operations.


