A well-structured shutdown and turnaround timeline is the backbone of the entire project. It will guide your team through the intricate process,
ensuring they meet objectives on time and efficiently. Let’s break down the various components of timeline development in greater detail.
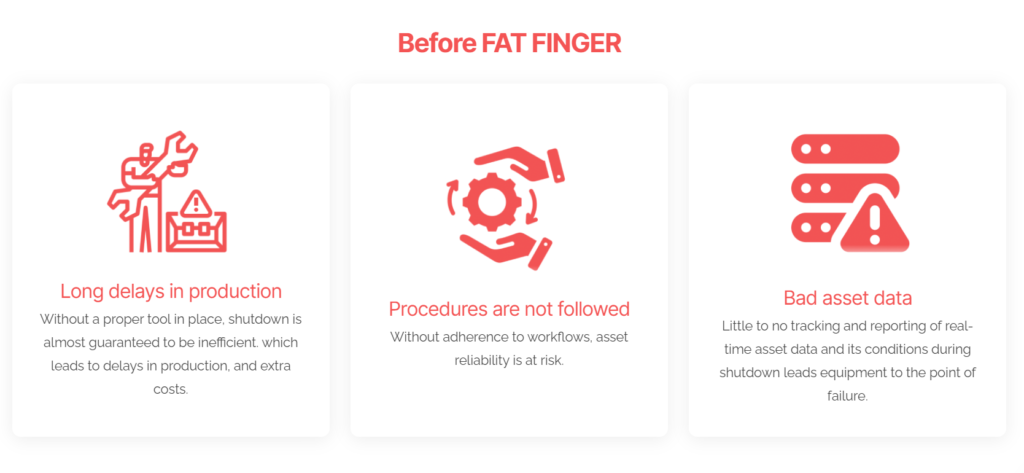
Why Use FAT FINGER to Plan Shutdowns and Turnarounds
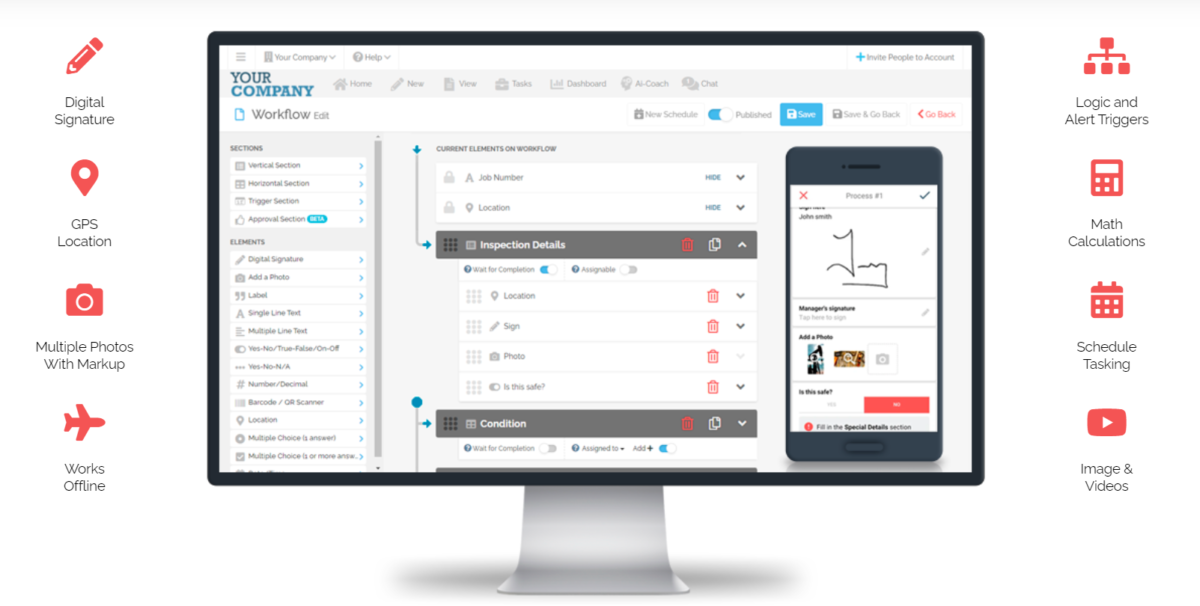
Thorough planning results in an accurate timeline, and as we’ve mentioned, an accurate timeline is important for your shutdown to succeed.
We recommend using FAT FINGER to develop your shutdown and turnaround timeline, to ensure complete visibility in real time throughout the entire process.
FAT FINGER features an easy-to-use, no-code, drag-and-drop builder that helps organizations digitize procedures by building custom workflows.
Below are reasons why you should use FAT FINGER:
Streamline Data Collection
Capture data accurately and in real time, and eliminate errors
Increase Efficiency
Automating shutdowns and turnarounds with FAT FINGER saves time and resources.
Integrate with AR and IoT
By integrating with AR, your team can take advantage of immersive visual guides and inspect difficult to reach areas.
You can integrate data from your IoT devices into FAT FINGER to leverage the full potential of your data, such as repair history and SOPs, for better decision-making in shutdowns.
Customized Dashboards
Collect and view all your data in one centralized place.
5 Procedures to Include in Your Timeline
Creating a comprehensive timeline is essential for a successful shutdown and turnaround. This timeline should include the following components:
- Pre-Shutdown Activities: These include inspections, repairs, and any pre-shutdown maintenance.
- Shutdown Procedures: The actual suspension of operations and commencement of maintenance and repair work.
- Turnaround Activities: These are the core activities during the shutdown, such as equipment inspections, overhauls, and upgrades.
- Post-Turnaround Inspections: These are the checks you should conduct after the TAR, to ensure you’ve met all objectives.
- Restart Procedures: The safe and efficient re-initiation of operations.
1- Pre-Shutdown Activities
Before the actual shutdown begins, complete these essential pre-shutdown activities:
a. Equipment Inspection and Assessment
Thoroughly assessing the condition of all equipment and assets is paramount. This step involves identifying any signs of wear and tear, potential issues, or areas that require immediate attention. This detailed inspection allows for targeted maintenance and repairs during the shutdown.

b. Maintenance and Repairs
Develop a plan for pre-shutdown maintenance and repairs based on the findings from the inspections. This may include tasks such as replacing worn components, performing routine maintenance, and addressing any issues that could impact the safety or efficiency of operations.
c. Resource Allocation
Allocating the necessary resources, both in terms of personnel and materials, is a vital pre-shutdown activity. Ensuring that the right people and equipment are in place when the shutdown commences is crucial for minimizing downtime.
2 – Shutdown Procedures
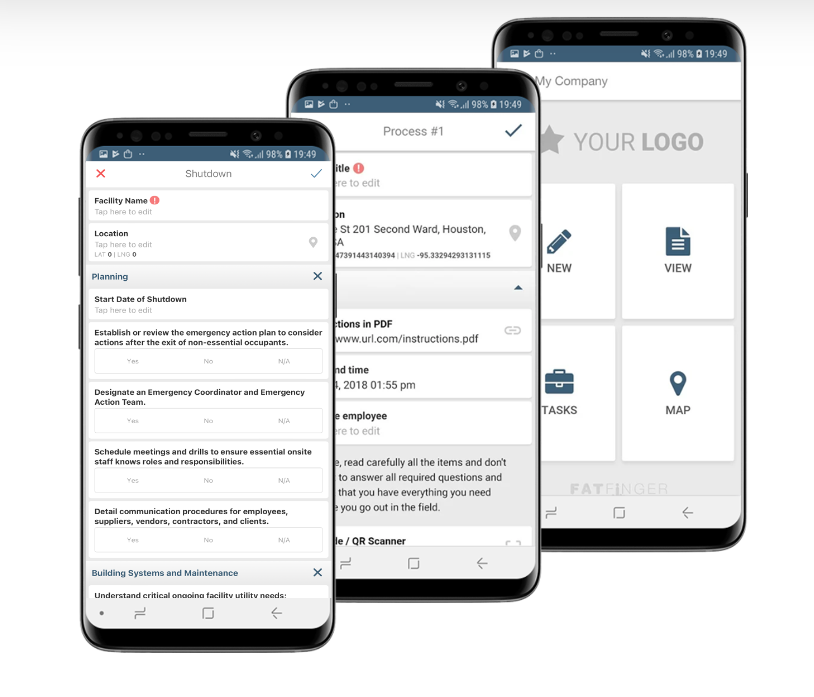
The actual shutdown process is a critical phase, often involving several key steps:
a. Suspension of Operations
This is the point where regular operations cease. It’s a carefully coordinated process to ensure that all systems are safely powered down, and equipment is secure. Any remaining products are often processed or stored to prevent wastage.
b. Safety Measures
Safety is paramount during the shutdown process. This includes ensuring that all equipment is depressurized, locked out, and tagged out to prevent accidents. Your shutdown team must also adhere to strict safety protocols to protect themselves during this phase.
3. Turnaround Activities
The core of the shutdown and turnaround operation, this phase includes extensive activities such as:
a. Equipment Inspections
You and your team should carry out in-depth inspections of all equipment and assets are carried out. If you use AR glasses in your work, this would be a good time to integrate it with FAT FINGER, to identify hidden defects or weaknesses.
b. Repairs and Upgrades
Address issues identified during inspections by repairing or replacing faulty components and executing upgrades to enhance equipment performance, safety, and efficiency.
4 – Post-Turnaround Inspections
After completing the turnaround activities conduct thorough post-turnaround inspections. This phase serves to verify that all the objectives set at the beginning of the project have been met. It includes:
a. Quality Assurance
Carefully review the work carried out during the turnaround to ensure it meets the highest quality standards. This is essential to guarantee the longevity and reliability of equipment.
b. Safety Checks
Conduct safety checks to ensure that all systems are in place and functioning correctly. The goal is to maintain a safe working environment when regular operations resume.
5 – Restart Procedures
The final phase of the timeline involves the safe and efficient restart of operations. This is not merely a matter of switching everything back on. It includes:

a. System Checks
Methodically test each piece of equipment and every process to confirm everything functions correctly. Address any deviations or issues before full-scale operations resume.
b. Operational Optimization
The restart phase is also an opportunity to optimize operations. Apply lessons learned during the shutdown and turnaround, to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime in the future.