In the oil and gas industry, safety and risk management are paramount. One critical aspect of ensuring safety is understanding and managing hazardous areas, particularly Zone 21.
This article delves into what Zone 21 is, its relevance in the oil and gas sector, and how digital workflows like FAT FINGER can enhance safety and compliance.
Request a demo of FAT FINGER to see how it can revolutionize your safety protocols.
Understanding Zone 21
Zone 21 is a classification used to identify areas where combustible dust clouds are likely to occur during normal operations. These areas are defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the IEC 60079-10-2 standard. In Zone 21, the presence of combustible dust is frequent enough to pose a significant risk of explosion.
Characteristics of Zone 21
- Frequent presence of combustible dust clouds
- High risk of ignition and explosion
- Requires stringent safety measures
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for implementing effective safety measures. The oil and gas industry often deals with materials that can create hazardous dust, making Zone 21 a critical area of focus.
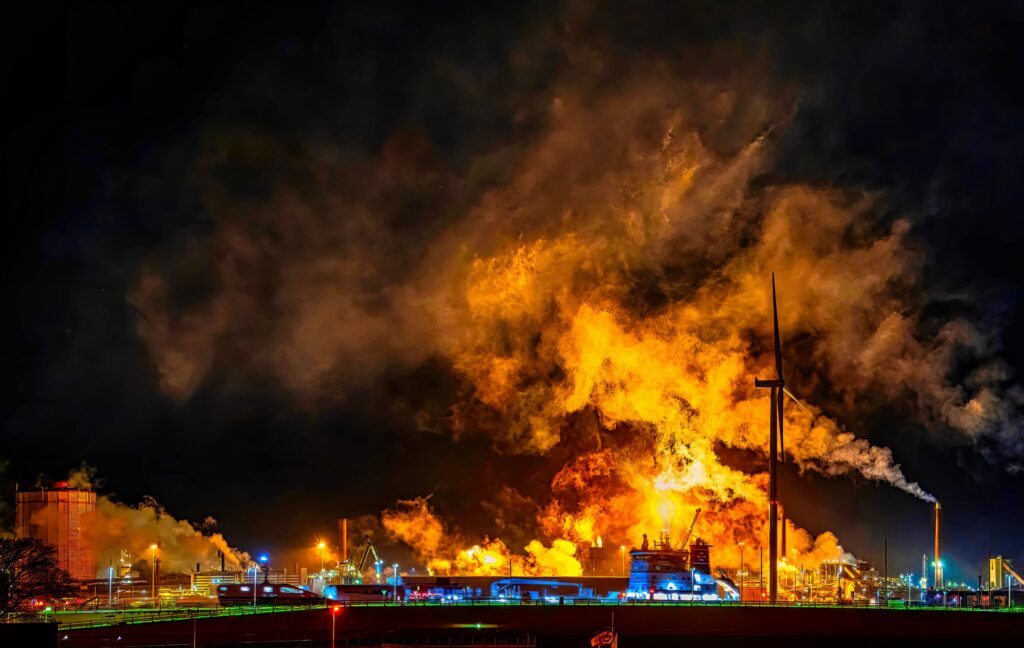

Relevance of Zone 21 in Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry is fraught with potential hazards, and Zone 21 is particularly relevant due to the nature of the materials handled. Combustible dust can originate from various sources, including drilling operations, material handling, and processing activities.
Examples of Combustible Dust in Oil and Gas
- Drilling muds and cuttings
- Processing residues
- Storage and handling of materials
These examples highlight the need for stringent safety protocols in Zone 21 areas. Failure to manage these risks can lead to catastrophic incidents, including explosions and fires.
Case Studies: Zone 21 Incidents in Oil and Gas
Several incidents in the oil and gas industry underscore the importance of managing Zone 21 hazards. For instance, a dust explosion at a processing facility resulted in significant damage and injuries. Investigations revealed inadequate safety measures and poor risk assessment.
Lessons Learned
- Importance of regular safety audits
- Need for comprehensive risk assessments
- Implementation of effective safety protocols
These lessons emphasize the need for robust safety management systems to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Enhancing Safety in Zone 21 with FAT FINGER
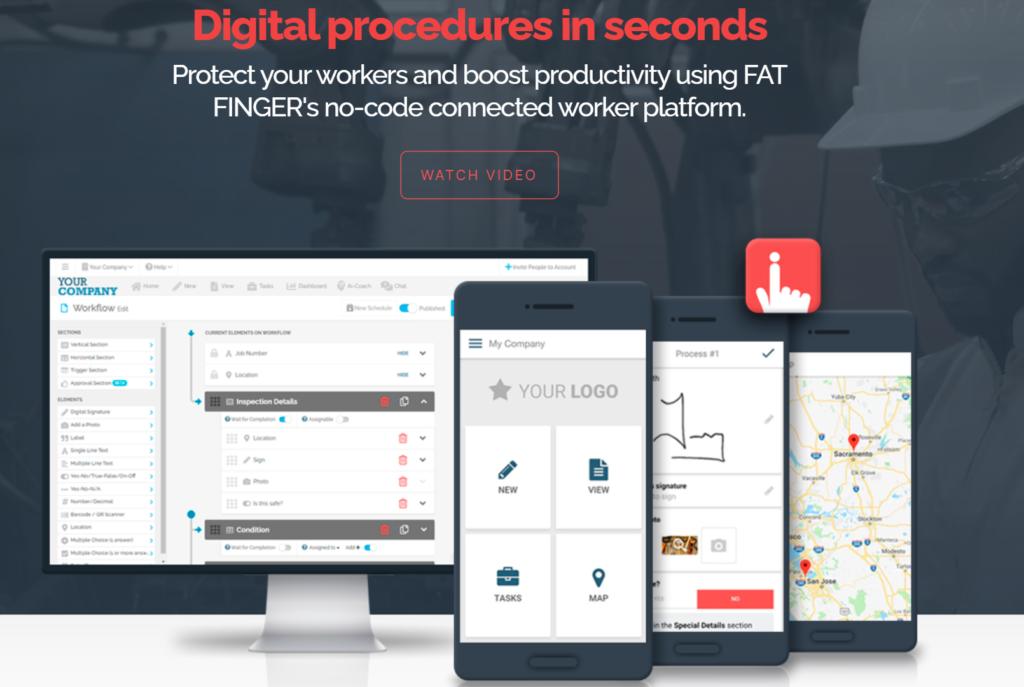
Managing safety in Zone 21 areas requires a comprehensive approach. Digital workflows like FAT FINGER offer a powerful solution to enhance safety and compliance.
FAT FINGER provides six powerful safety checklists that can be tailored to your specific needs.
1. Take 5 Safety
The Take 5 Safety checklist encourages workers to take five minutes to assess potential hazards before starting a task. This proactive approach helps identify and mitigate risks in Zone 21 areas.
2. Near Miss Reporting
Near miss reporting is crucial for identifying potential hazards before they result in incidents. FAT FINGER’s Near Miss Reporting checklist makes it easy to document and analyze near misses, helping to prevent future incidents.
3. Job Hazard Analysis
Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) involves identifying and evaluating hazards associated with specific tasks. FAT FINGER’s JHA checklist ensures that all potential risks in Zone 21 areas are thoroughly assessed and managed.
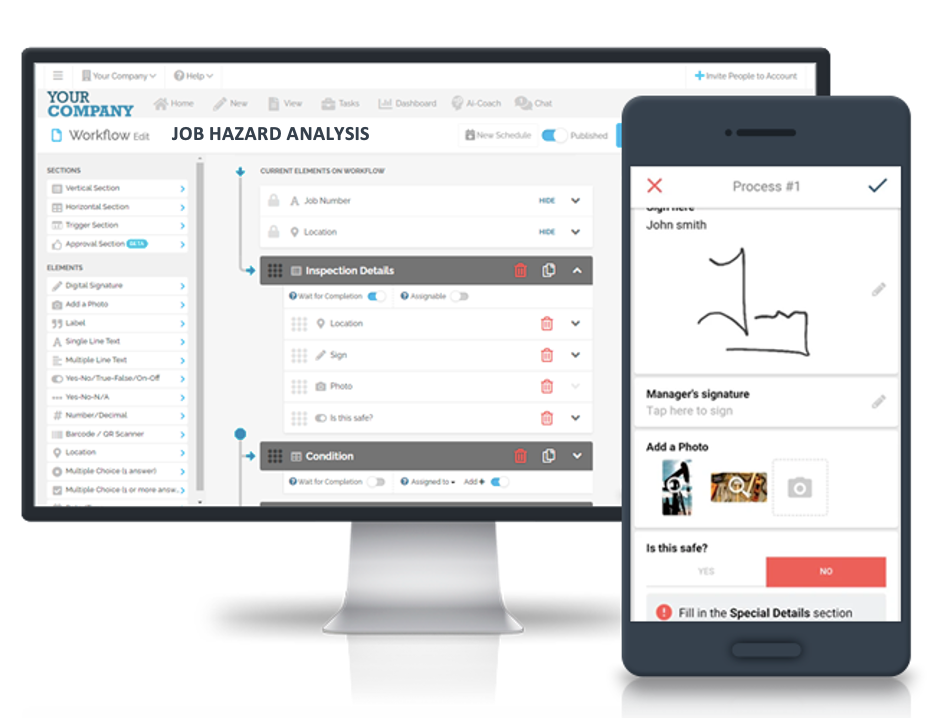
4. Risk Assessment
Effective risk assessment is essential for managing Zone 21 hazards. FAT FINGER’s Risk Assessment checklist provides a structured approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks.
5. Incident Reporting
Timely and accurate incident reporting is critical for improving safety. FAT FINGER’s Incident Reporting checklist streamlines the reporting process, ensuring that all incidents are documented and analyzed.
6. Journey Report
The Journey Report checklist helps manage risks associated with transportation and logistics. This is particularly relevant in the oil and gas industry, where materials are frequently moved through Zone 21 areas.
Conclusion
Zone 21 is a critical area of focus in the oil and gas industry due to the high risk of combustible dust explosions. Understanding the characteristics and relevance of Zone 21 is essential for implementing effective safety measures. Digital workflows like FAT FINGER offer powerful tools to enhance safety and compliance in these hazardous areas.
By leveraging FAT FINGER’s six powerful safety checklists, you can proactively manage risks and ensure a safer working environment. Create a safety workflow for free on FAT FINGER or request a demo to see how it can revolutionize your safety protocols.

