In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, efficient and accurate inspections are more critical than ever. Traditional inspection methods often fall short, leading to costly errors and downtime. Fortunately, advanced inspection techniques in oil and gas, powered by cutting-edge technology, are revolutionizing the way inspections are conducted. This article delves into these advanced techniques, highlighting their benefits and showcasing how digital workflows like FAT FINGER can streamline the inspection process. Request a demo today to see how FAT FINGER can transform your inspection procedures.
The Evolution of Inspection Techniques
Inspection techniques have come a long way from manual checklists and visual assessments. The advent of technology has introduced a plethora of tools and methods that enhance accuracy, efficiency, and safety. These advancements are not just incremental improvements; they represent a paradigm shift in how inspections are performed.
Traditional Inspection Methods
Traditional inspection methods often rely on human judgment and manual processes. While these methods have served industries for decades, they come with inherent limitations:
- Human error and subjectivity
- Time-consuming processes
- Inconsistent documentation
- Limited data analysis capabilities
These limitations can lead to missed defects, increased downtime, and higher operational costs. The need for more reliable and efficient inspection methods has never been more apparent.
Advanced Inspection Techniques in Oil and Gas
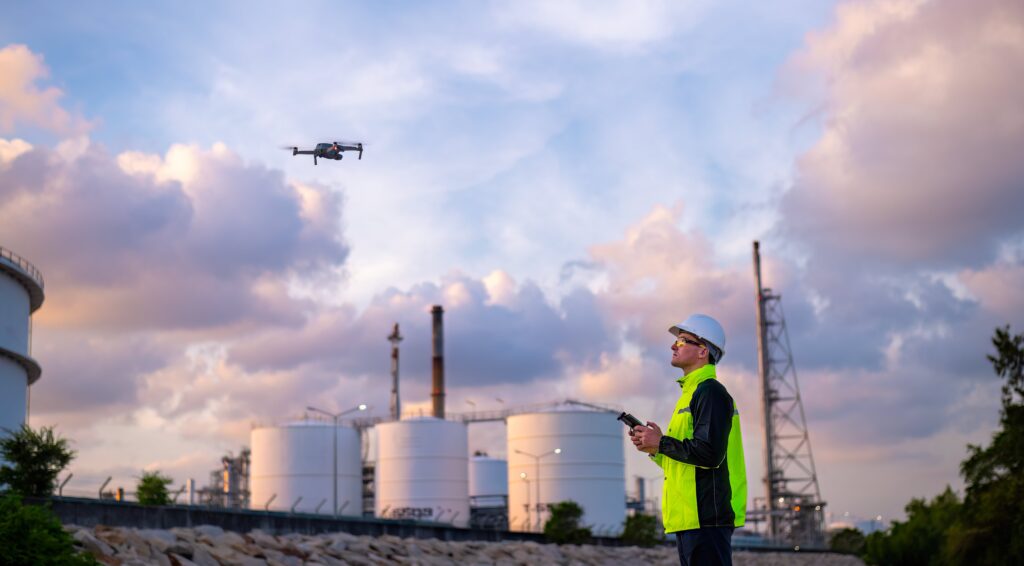

Technological advancements have introduced a range of tools and techniques that address the shortcomings of traditional methods. These include:
- Non-destructive testing (NDT)
- Automated inspection systems
- Drone inspections
- Machine learning and AI
- Digital workflows
Each of these technologies brings unique benefits, enhancing the overall inspection process. Let’s explore these advanced techniques in more detail.
Digital Workflows: The Future of Inspections
Digital workflows are revolutionizing the inspection process by streamlining data collection, analysis, and reporting. Platforms like FAT FINGER enable organizations to create customized digital workflows that enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Benefits of Digital Workflows
Digital workflows offer numerous advantages over traditional paper-based methods:
- Real-time data capture and synchronization
- Automated reporting and documentation
- Enhanced collaboration and communication
- Improved compliance and auditability
- Integration with other tools and IoT
- AI Coaching
FAT FINGER, for example, allows users to create mobile asset inspection workflows that can be accessed and completed on any device. This ensures that inspections are conducted consistently and that data is readily available for analysis and decision-making.
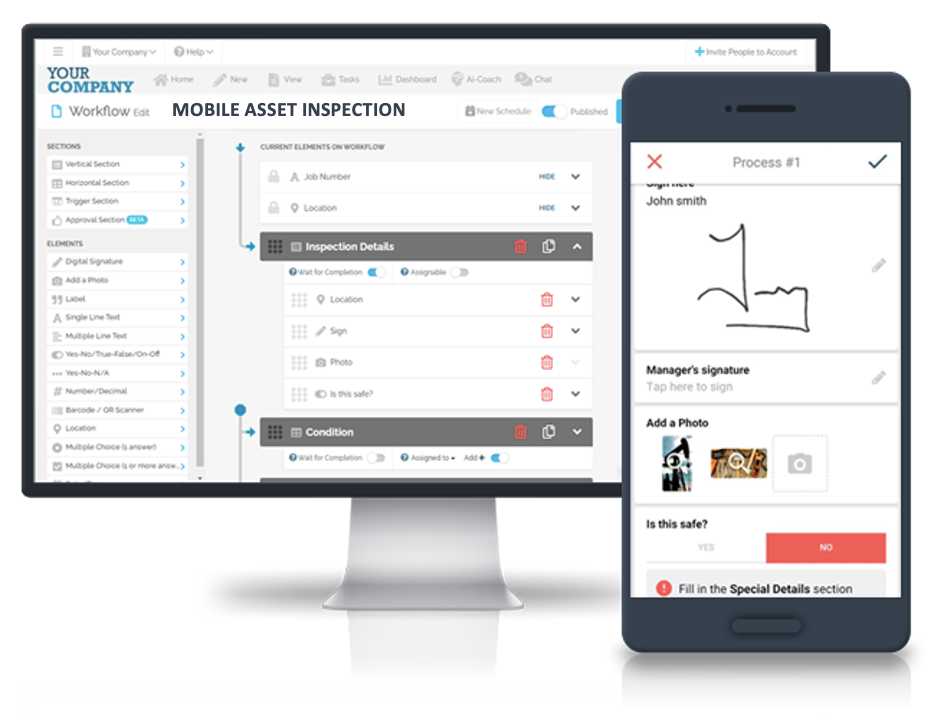
Case Study: FAT FINGER in Action
Consider a manufacturing company that implemented FAT FINGER to streamline its inspection processes. By transitioning from paper-based checklists to digital workflows, the company achieved the following results:
- Reduced inspection time by 30%
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is a cornerstone of modern inspection techniques. NDT methods allow inspectors to evaluate the integrity of materials and structures without causing damage. This is particularly valuable in industries where safety and reliability are paramount, such as aerospace, oil and gas, and manufacturing.
Types of NDT Methods
NDT encompasses a variety of techniques, each suited to specific applications:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): Employs X-rays or gamma rays to create images of internal structures.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): Detects surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT): Reveals surface-breaking defects through the application of a liquid dye.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): Utilizes electromagnetic induction to detect surface and sub-surface flaws.
These methods provide valuable insights into the condition of assets, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of catastrophic failures.
Automated Inspection Systems
Automated inspection systems leverage robotics and advanced imaging technologies to perform inspections with unparalleled precision and speed. These systems are particularly useful in environments that are hazardous or difficult for human inspectors to access.
Benefits of Automation
Automated inspection systems offer several key advantages:
- Increased accuracy and repeatability
- Reduced inspection time
- Enhanced safety for inspectors
- Comprehensive data collection and analysis
For example, in the automotive industry, automated systems can inspect welds and components with high precision, ensuring quality and compliance with stringent standards.
Drone Inspections
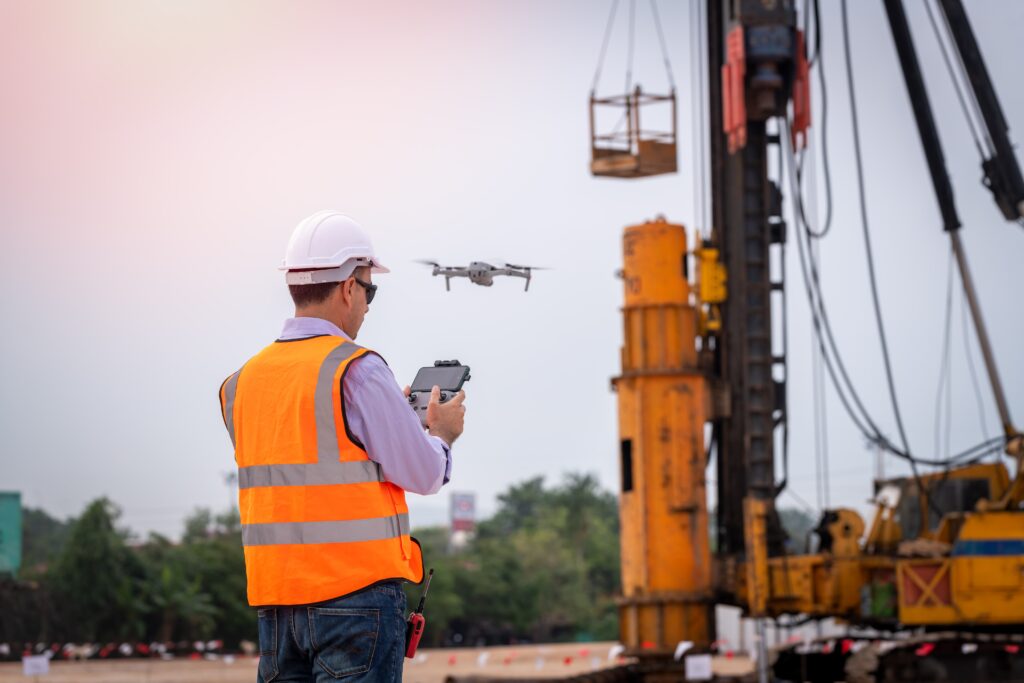

Drones have emerged as a game-changer in the field of inspections. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones can access hard-to-reach areas and capture detailed images and data.
Applications of Drone Inspections
Drones are used in a variety of industries for inspection purposes:
- Infrastructure: Inspecting bridges, towers, and pipelines.
- Energy: Monitoring wind turbines, solar panels, and power lines.
- Construction: Surveying construction sites and monitoring progress.
- Oil and Gas: Inspecting offshore platforms and refineries.
Drone inspections not only improve safety by reducing the need for human inspectors to work at heights or in hazardous conditions but also provide comprehensive data that can be analyzed to identify potential issues.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the inspection landscape by enabling predictive maintenance and real-time anomaly detection. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential failures before they occur.
AI-Powered Inspection Solutions
AI-powered inspection solutions offer several benefits:
- Real-time data analysis and anomaly detection
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs
- Improved decision-making through data-driven insights
For instance, in the manufacturing sector, AI can analyze data from sensors on production lines to detect deviations from normal operating conditions, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing disruptions.
Benefits of Advanced Inspection Techniques in Oil and Gas
The benefits of advanced inspection techniques include the following:
Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
One of the primary benefits of advanced inspection techniques is the significant enhancement in accuracy and precision. Traditional inspection methods often rely on manual processes that are prone to human error. In contrast, modern technologies such as drones, robotic systems, and advanced imaging techniques provide highly accurate data that can be analyzed with precision. For instance, drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture detailed images of hard-to-reach areas, allowing for thorough inspections without the need for scaffolding or other costly infrastructure.
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Advanced inspection technologies drastically reduce the time required to conduct inspections. Automated systems can perform inspections continuously and at a much faster pace than human inspectors. For example, automated ultrasonic testing or laser scanning can quickly assess the integrity of materials and structures, providing immediate feedback and reducing downtime. This increased speed not only enhances productivity but also allows for more frequent inspections, thereby ensuring ongoing compliance with safety and regulatory standards.
Cost-Effective Solutions
While the initial investment in advanced inspection technology may be significant, the long-term cost savings are substantial. Automated inspection systems reduce the need for extensive manual labor, decrease operational downtime, and minimize the risk of costly errors or oversights. Additionally, the ability to detect potential issues early through regular and precise inspections can prevent expensive repairs and extend the lifespan of assets.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Advanced inspection techniques generate large volumes of data that can be leveraged for informed decision-making. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms can analyze this data to identify patterns, predict potential failures, and recommend proactive maintenance strategies. This data-driven approach enables businesses to optimize their operations, allocate resources more effectively, and enhance overall asset management.
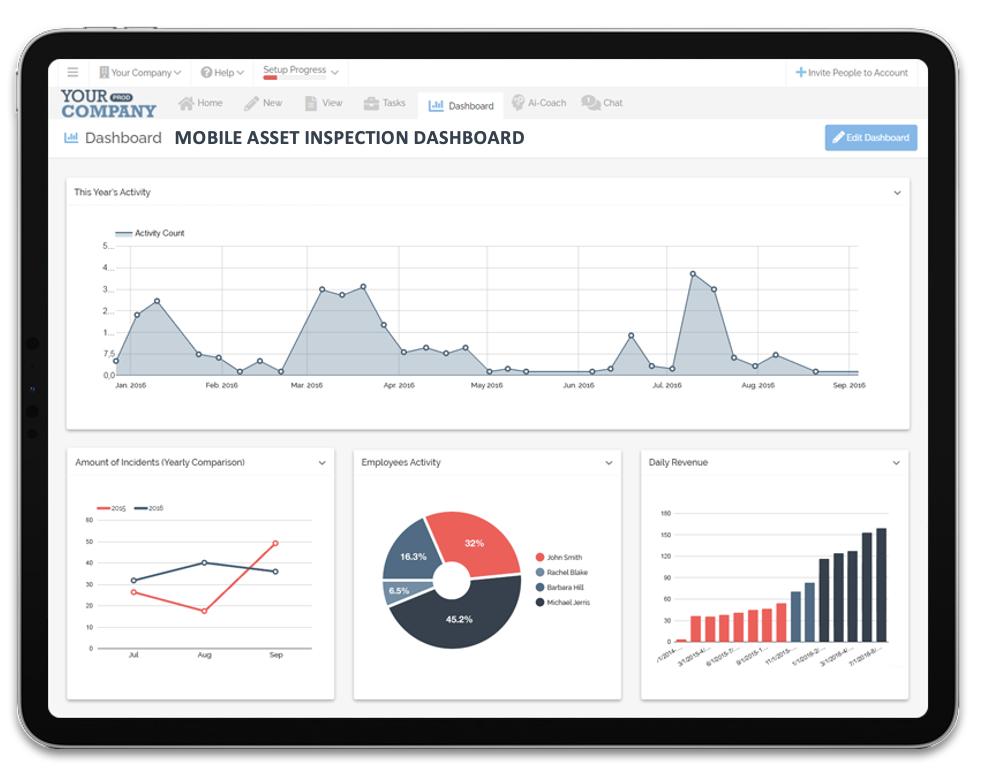
Improved Safety and Compliance
Safety is paramount in any inspection process, and advanced technologies play a crucial role in enhancing safety standards. Automated systems can perform inspections in hazardous or difficult environments, reducing the risk to human inspectors. Additionally, the ability to conduct non-destructive testing (NDT) ensures that inspections do not compromise the integrity of the asset being examined. Compliance with regulatory standards is also more easily achieved with precise and reliable inspection data.
Conclusion: Future of Advanced Inspection Techniques in Oil and Gas
The field of inspection technology is continually advancing, with new innovations emerging regularly. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) is set to further transform inspection processes. IoT-enabled sensors can provide real-time monitoring and diagnostics, while AR and VR technologies can offer immersive training experiences and remote inspection capabilities. As these technologies continue to evolve, the potential for even greater efficiencies and improvements in inspection processes becomes increasingly attainable.

